The North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) is a not-for-profit international regulatory authority whose mission is to assure the effective and efficient reduction of risks to the reliability and security of the grid. NERC was formed in 2006 as the successor to the North American Electric Reliability Council (which, confusingly, was also called NERC).
NERC was formed in response to the August, 2003 blackout in the north-eastern US and Ontario, Canada, affecting 50 million people.
NERC oversees the Mandatory Reliability Standards (MRS) program that sets standards for electric utilities to improve grid reliability in North America. These standards originally focused on vegetation management (the cause of the 2003 blackout), but have since extended to cover other reliability issues such as cybersecurity.
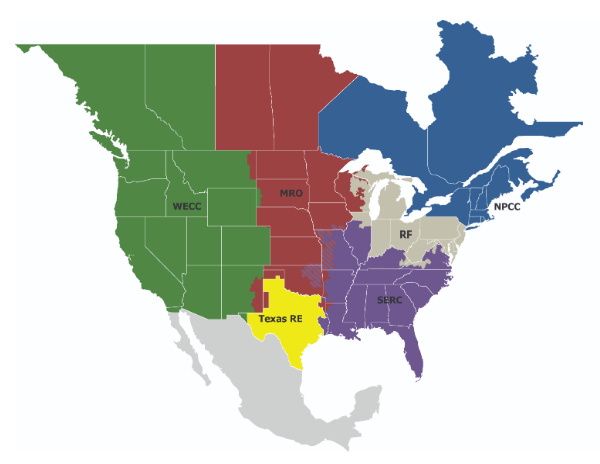
NERC’s responsibilities cover the following regions:
NERC in BC
According to section 125.2 of the Utilities Commission Act, the BCUC has “exclusive jurisdiction to determine whether a reliability standard is in the public interest and should be adopted in British Columbia.” However, the BCUC works with both NERC and the Western Electricity Coordinating Council Inc. (WECC) to develop and adopt reliability standards in BC, and to monitor and enforce compliance with those standards.
There is a memorandum of understanding (MOU) between NERC, WECC and the BCUC governing the relationship between the three organizations.
NERC is responsible for developing the MRS standards, and filing them with the BCUC. In turn, the BCUC adopts and enforces the standards in BC.
WECC assists the BCUC with its compliance responsibilities according to the terms of the Administration Agreement between the two organizations.

